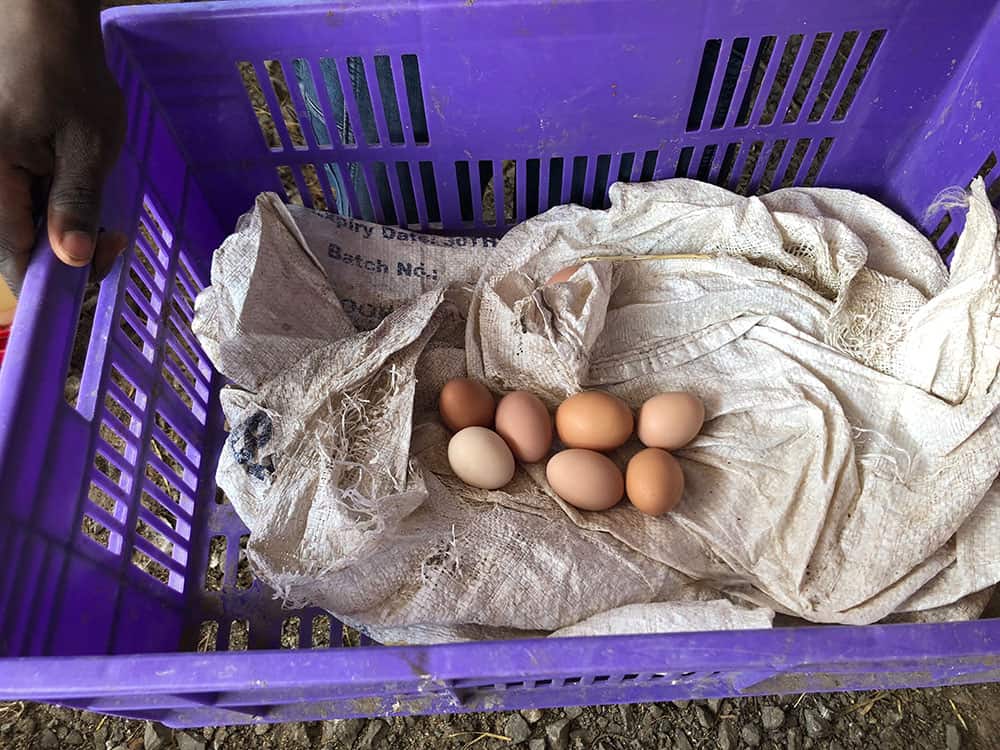
The Masai farm in Olpirikata has been in operation since August 2017 and was already autonomous five months later, meaning that the ten men who work on the farm can already be paid from the sale of milk.
But we also have chickens on the farm and there is a microfinancing project connected to this that we will be presenting soon. To get you in the mood for this and in view of the approaching Easter celebrations, we have put together a few facts and figures about eggs.
Happy reading!
How many eggs does a chicken lay?
A chicken lays about one egg a day. The egg is built up from the yolk to the outside within 24 hours. However, hens only use the left ovary. The right one atrophies. This results in an average of 280 eggs in a year. The hen does not lay any eggs during moulting, when it changes its plumage, which may not look very pretty, but is completely natural.
What determines the color of the eggs?
The color of the eggs is genetically determined and does not depend on the plumage of the hens or the feed, no, it depends on the ears of the animals. More precisely, the egg color is determined by the ear discs, which are the flaps of skin under the ear that lie directly behind the eyes. Hens with white ear discs lay white eggs and hens with red ear discs lay brown eggs. There are also so-called green layers, which are domestic hens that lay eggs with green to turquoise-colored eggshells. The ear disks of these green layers are also red.
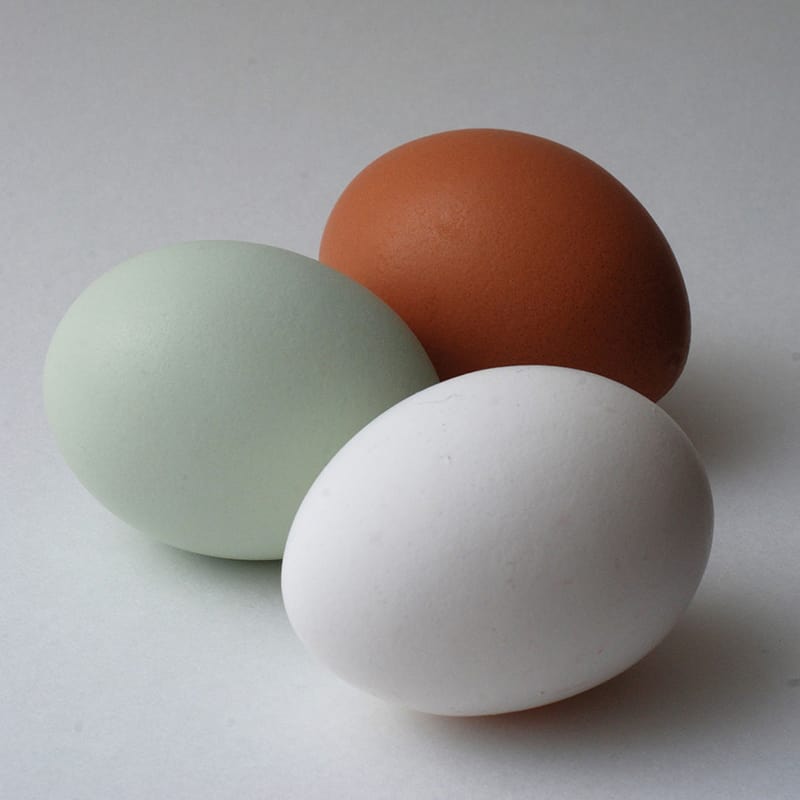

How does the color get into the eggs?
The different colors are caused by the storage of color pigments in the eggshell, which consists of lime. White eggs therefore contain no pigments in the shell.1) The green color of the eggs is due to the bile pigment oocyanin. 2)
The so-called shell gland in the hen’s laying intestine is responsible for coloring the eggs. It ensures that color pigments are stored in the calcium shell, which were previously produced as a breakdown product from blood or bile and temporarily stored in the liver. When all the pigments come together, the egg color is brown. If the chicken lacks the gene responsible for color formation, it lays white eggs.
However, the color of the eggs does not affect the taste or nutritional value of the eggs. The nutrition, husbandry and genetics of the hen are responsible for this.
Why is the egg not round?
A raw egg is not nearly as delicate as it seems. Despite a shell thickness of just 0.4 mm, it is impossible to crush an egg held upright between the fingers of one hand, and even an egg lying flat is almost impossible to “break”. The reason for this is its curved shape, which means that the pressure exerted on one part of the shell is distributed evenly over the whole egg. The egg’s high resistance is of course also designed to withstand the weight of the hen during incubation.
However, the stability of the curved shape also applies to a sphere. The reason why nature has opted for a different packaging design is that round eggs would roll away much more easily if they fell out of the nest. 3) Incidentally, you can easily try this out for yourself: If you take a ball and an egg and place them both on a table, the ball will roll for a long time after being pushed and may even fall over the edge of the table onto the floor. The egg, on the other hand, describes a curve and rolls irregularly.
What does an egg contain?
Eggs are one of the most valuable animal foods. The biological value of eggs is higher than that of fish, meat and milk. The protein they contain helps the human body to produce important proteins for various bodily functions, provides energy and is important for building muscle.
Egg yolks are rich in vitamins (A, D, K, B12), protein, calcium, iron, fat and cholesterol. On average, the yolk makes up 42% of the weight of an egg.
The egg white consists largely of water and egg white and is deposited in phases of varying viscosity around the yolk. There are four different protein layers.
The so-called chalazae hold the yolk in its central position from the polar regions and thus ensure that the yolk does not adhere to the eggshell. In a fresh egg, the viscosity of the egg white is higher than in an old egg. The egg white makes up an average of 58% of the weight of an egg. 5)
Source: http://www.deutsche-eier.info/das-ei/aufbau/
How long do eggs last?
Fresh eggs have a minimum shelf life of 28 days after laying. Even after 28 days, eggs do not have to be thrown away. Old eggs should be heated to at least 70 degrees C so that they are safe for consumption.
Freshness tests
Float test: Place the whole egg in cold water – fresh eggs remain at the bottom.
Shaking test: If you shake a fresh egg close to your ear, you should not hear anything. If you hear a sloshing or a faint muffled sound, then the egg is already older.
Cracking test: In a fresh egg, the strongly curved yolk lies in the middle of the egg white. The viscous egg white forms a ring around the yolk. Older eggs have a flat, wide yolk, its membrane bursts easily and the egg white spreads out in a thin liquid.
Light test: If you hold a fresh egg up to a light source, you can just make out the bright air chamber on the blunt side of the egg. The yolk may already be recognizable without a solid outline. An older egg (more than two weeks old) has a larger air chamber and a clearly recognizable yolk.
Smell test: Spoiled eggs have a sulphurous smell.
What is the best way to store eggs?
Fresh eggs do not need to be stored in the fridge – unless the eggs are bought chilled from the supermarket. In this case, the cold chain should not be interrupted and the eggs should be kept in the fridge, as chilled eggs cannot tolerate large temperature fluctuations. If the temperature rises, condensation forms on the shell, which damages the cuticle. This allows germs to get inside the egg. However, storing eggs in the fridge protects the vitamins in the egg from light and oxygen. It is also important to store the eggs with the pointed end facing upwards. If the eggs are stored the other way round, the air bubble migrates and detaches the egg membrane, which in turn increases the risk of bacteria penetrating.
Why do eggs stay in the fresh air?
The approximately 10,000 pores on the shell give the calcite crystals of the shell a grid-like structure and act like a respiratory organ. An intact layer is covered with a thin layer, the cuticle, which prevents germs from penetrating the egg. However, water destroys this cuticle, the natural protective layer of eggs. Eggs should therefore never be washed before storage. 4)
Tips and tricks for handling eggs
- Best stored in a cardboard box, protected from light and oxygen.
- Do not place fresh eggs in direct sunlight.
- Extreme temperature fluctuations impair the natural self-protection of the ice cream, impair the quality and accelerate the ageing process.
- Eggs that have passed the best-before date of 28 days after laying should no longer be eaten raw. However, they can still be used for baking or cooking or as hard-boiled eggs when heated through to 70° C.
- Overcooking or cooking at over 90°C can lead to a chemical reaction between the iron in the egg yolk and the sulphur in the egg white, resulting in the formation of a greenish ring around the egg yolk.
- An egg only tastes best from the 4th day after laying.
- Always store eggs with the blunt end facing upwards, otherwise the air bubble and the egg yolk will shift. 6)
- Do not wash fresh eggs before storage – this destroys the natural protective layer.
- Do not store eggs near strong-smelling foods.
- Hard-boiled eggs are easier to peel when they are a little older, as this is associated with important chemical changes inside the shell. An older egg loses carbon dioxide through the fine pores of the eggshell, which changes the acidity inside the egg. 7)
- Cold quenching after cooking can reduce the shelf life of a hard-boiled egg. Normally, a hard-boiled egg will keep for up to a month, in the fridge even up to six weeks.
- Leftover egg yolks and egg whites can be frozen or stored in a small jar. To protect them from drying out, pour a little sunflower oil or cold water over them and place in the fridge.
- The eggshell can be used as fertilizer in the bed or composted.
References
- http://www.wirkochen.at/lexikon/Der-Unterschied-zwischen-braunen-und-weissen-Eiern/240782411
- Wikipedia: https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/oocyan
- http://www.daserste.de/information/wissen-kultur/w-wie-wissen/sendung/2010/die-perfekte-form-ei-100.html
- https://www.focus.de/gesundheit/praxistipps/eier-richtig-lagern-darauf-kommt-es-an_id_6931486.html.
- https://www.lebensmittellexikon.de/e0000520.php
- eggs.com
- Quoted from Thomas Vilgis, researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research in Mainz and expert on the physics of food, among other things, in the article “Why some eggs are difficult to peel” from 08.04.2012 https://www.welt.de/wissenschaft/article106156413/Warum-sich-manches-Ei-schwer-pellen-laesst.html